WARE FAMILY HISTORY
Wanda Ware DeGidio
wwdegidio@gmail.com www.warefamilyhistory.com
Wanda Ware DeGidio
wwdegidio@gmail.com www.warefamilyhistory.com
WARE DNA
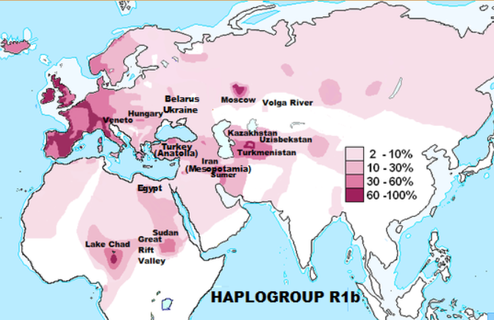
HAPLOGROUP R1B
(Specifically Haplogroup R-M269, also known as R1b1a1a2)
HAPLOGROUP R1B
(Specifically Haplogroup R-M269, also known as R1b1a1a2)
Haplogroup R1b are rare in Africa, being found mainly in Asia and Europe. A small group of chromosomes within the paragroup R-P25* are concentrated in the central-western part of the African continent, and detected up to 95%. Human Y chromosome haplogroup R-V88: a paternal genetic record of early mid Holocene trans-Saharan connections and the spread of Chadic languages. Eur J. Hum, Genet, 7/18/2010.
An R1b1 study, "Paleolithic Y-haplogroup heritage predominates in a Cretan highland plateau", by Laisel Martinex, and others, et al. (2007) is discussed. Referred by some as the birthplace of western civilization, the island of Crete ... is situated about equal distance from mainland Greece, Turkey and Libya ... inhabitants of the island of Crete arrived about 9,000 BCE, possibly from Anatolia. This founding group was mainly composed of early Neolithic farmers who established their first settlements in the fertile lowland regions. 4,000 years later, this population in part formed the basis of what has since been termed the Minoan culture, a civilization that prospered from mercantilism and trade with other Mediterranean civilizations. Y-STR-based analyses show the close affinity that R1a1 chromosomes from the Lasithi Plateau (Crete and Greece) shared with those from the Balkans, but not with those from lowland eastern Crete. In contrast, Cretan R1b microsatellite-defined haplotypes displayed more resemblance to those from Northeast Italy than to those from Turkey and the Balkans (territories of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Kosovo, the Republic of Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia and Slovenia).
An R1b1 study, "Paleolithic Y-haplogroup heritage predominates in a Cretan highland plateau", by Laisel Martinex, and others, et al. (2007) is discussed. Referred by some as the birthplace of western civilization, the island of Crete ... is situated about equal distance from mainland Greece, Turkey and Libya ... inhabitants of the island of Crete arrived about 9,000 BCE, possibly from Anatolia. This founding group was mainly composed of early Neolithic farmers who established their first settlements in the fertile lowland regions. 4,000 years later, this population in part formed the basis of what has since been termed the Minoan culture, a civilization that prospered from mercantilism and trade with other Mediterranean civilizations. Y-STR-based analyses show the close affinity that R1a1 chromosomes from the Lasithi Plateau (Crete and Greece) shared with those from the Balkans, but not with those from lowland eastern Crete. In contrast, Cretan R1b microsatellite-defined haplotypes displayed more resemblance to those from Northeast Italy than to those from Turkey and the Balkans (territories of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Kosovo, the Republic of Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia and Slovenia).
The Arbins (bearers of R1b haplogroup) along their migration route to the Middle East and South Mesopotamia apparently have established the Sumer culture (and the state), moving westward to Europe (5000-4500 ybp) carrying mainly the R-M269 subclade and its downstream L23 subclade. This last subclade was nearly absent along the North African route, and/or did not survive the migration to Iberia or evidenced later. At the arrival to Iberia (4800 ybp) the M269 subclade split off M51 and soon thereafter the L11 downstream subclades. These populations became known as the Bell Beakers and moved north, along with the newly arisen subclades of P312 and L21 (which split off within a few centuries after P312). Ancient History of the Arbins, Bearers of Haplogroup R1b, from Central Asia to Europe, 16,000 to 1500 Years before Present, By Anatole A. Klyoso, 2012.
From my research, Klyoso is correct in placing R1b in the ancient region of Mesopotamia prior to R1b moving on to other areas of the Middle East. These early cultures were relaxed in allowing different tribes to embrace their idea of a city-state in order to remain independent of one another and fully self-reliant. During times of drought or conflict, one or more tribes could move on to a new location, while the remaining city-states continued to be a cohesive defense against outside aggression. Even after leaving the city-state for a new location, it's likely there was continuing communication and trade between the various tribes.
Phylogenetic tree of Haplogroup R1b with defining mutations - R1b-M343, R1b1-P25, Black Sea R1b1a-P297, Pontic Steppe R1b1a2-M269. This Ware family is haplogroup R1b1a2 or R-M269.
R1b1 (R-L278*) Villabruna 1 (Belluno Province) was found in the small rockshelter named Riparo Villabruna A in the Veneto Dolomites. It was an Epigravettian culture in the Cismon valley (Veneto, Italy) and the remains were dated to c. 14,000 BP.
In the Dolomite Mountains 51 remains were found, of which the results of the only haplogroup R1b1 is provided here. The Dolomite Mountains located in northwestern Italy form part of the Southern Limestone Alps. Sample Code: Villabruna, Date Source: New, Country: Italy, Lat, Long.: 46.15 12.21, Cat BP 95.4%: 14,180-13,780, Date type (ref.): Direct UF (*), Culture: Epigravettian, Remain tested: Femur bone, SNP Panel: 3.7 M, Sex:M, mtDNA hg: U5b2b, Yhg.: R1b1(a*), Genetic Cluster: Villabruna, Damage Restrict: No, Mean Cov+: 3.137, SNP Covered: 1,215,433, Vercellotti, Alciati, Richards, Formicola (2008).
The Late Upper Paleolithic skeleton called Villabruna 1, is a "source of data on biology and behavior of a 14,000 year-old hunter". An interesting part of the paper is the "blue-eyed, dark-skinned man from Villabruna Cave 1, dated to ~ 14,000 years ago and belonging to paternal haplogroup R1b1". From these results, it appears blue eyes arose prior to 14,000 years ago, and begin to spread at that time. Pale skin only appeared across much of the continent after 7,000 years ago - borne by early farmers from the Near East. Journal of Anthropological Sciences. Vol. 86 (2008), pp. 143-163. He was buried with equipment of a hunter-gatherer including a fire stone knife, a fire stone core, another stone as hammer, a blade of fire stone, a bone tip, a pellet of ochre and Propolis (a resinous matter, produced by bees). Limestone platelets decorated with ochre drawings had been placed on top of the tomb. Villabruna is significant in terms of the history of population genetics: the remains were found to carry Y-DNA haplogroup R1b1a (R-L754). This is the oldest example documented of haplogroup R1b in Western Europe. Ripari Villabruna - Wikipedia.
R1b1 (R-L278*) (7640-7555 BP) The ‘Samara hunter-gatherer’ found is an adult male from grave 1 in a Neolithic-Eneolithic settlement producing artifacts from the Elshanka, Samara, and Repin cultures. The specific site is Lebyazhinka IV, on the Sok River, Samara oblast, Russia in the Volga region. Lebyazhinka IV and the neighboring Lebyazhinka V site were occupied seasonally by multiple cultures between 9000-5500 BP.
R1b (R-M269) a single male Bell Beaker R1b M269 from Quedlinburg, Germany dated to 6250 BP. An overview of sources from southern Germany concluded that Bell Beaker was a new and independent culture in that area.
R1b (R-M269) The remains of two males from a Bell Beaker German site at Kromsdorf dated to 6550 BP tested positive for R1b M269. It is known from other testing that R1b1a2 (R-M269) is the dominant branch of R1b in Western Europe.
R1b (R-M343) Lichtenstein Cave in Austria, near the border of Switzerland 1,000 BC - Out of the 19 males represented in the cave, 15 yielded the full 12 tested STR values, with 12 showing haplotypes related to I2b2 (at least four lineages), two to R1a (probably one lineage), and one to R1b predicted haplogroups. Mitochondrial haplogroups found included 17 from H, 5 from T2, 9 from U5b and 5 from J*.
R1b1a2 - King Tut (c.1341 BC - c.1323 BC) - A Swiss genealogy company named IGENEA issued a press release based on a blurry screen-grab from the Discovery documentary. It claimed that the colored peaks on the computer screen proved that Tutankhamun belonged to an ancestral line, or haplogroup called R1b1a2 [dated to 3340 BP], that is rare in modern Egypt but common in western Europeans. King Tut's DNA, By Analee Newitz.
From my research, Klyoso is correct in placing R1b in the ancient region of Mesopotamia prior to R1b moving on to other areas of the Middle East. These early cultures were relaxed in allowing different tribes to embrace their idea of a city-state in order to remain independent of one another and fully self-reliant. During times of drought or conflict, one or more tribes could move on to a new location, while the remaining city-states continued to be a cohesive defense against outside aggression. Even after leaving the city-state for a new location, it's likely there was continuing communication and trade between the various tribes.
Phylogenetic tree of Haplogroup R1b with defining mutations - R1b-M343, R1b1-P25, Black Sea R1b1a-P297, Pontic Steppe R1b1a2-M269. This Ware family is haplogroup R1b1a2 or R-M269.
R1b1 (R-L278*) Villabruna 1 (Belluno Province) was found in the small rockshelter named Riparo Villabruna A in the Veneto Dolomites. It was an Epigravettian culture in the Cismon valley (Veneto, Italy) and the remains were dated to c. 14,000 BP.
In the Dolomite Mountains 51 remains were found, of which the results of the only haplogroup R1b1 is provided here. The Dolomite Mountains located in northwestern Italy form part of the Southern Limestone Alps. Sample Code: Villabruna, Date Source: New, Country: Italy, Lat, Long.: 46.15 12.21, Cat BP 95.4%: 14,180-13,780, Date type (ref.): Direct UF (*), Culture: Epigravettian, Remain tested: Femur bone, SNP Panel: 3.7 M, Sex:M, mtDNA hg: U5b2b, Yhg.: R1b1(a*), Genetic Cluster: Villabruna, Damage Restrict: No, Mean Cov+: 3.137, SNP Covered: 1,215,433, Vercellotti, Alciati, Richards, Formicola (2008).
The Late Upper Paleolithic skeleton called Villabruna 1, is a "source of data on biology and behavior of a 14,000 year-old hunter". An interesting part of the paper is the "blue-eyed, dark-skinned man from Villabruna Cave 1, dated to ~ 14,000 years ago and belonging to paternal haplogroup R1b1". From these results, it appears blue eyes arose prior to 14,000 years ago, and begin to spread at that time. Pale skin only appeared across much of the continent after 7,000 years ago - borne by early farmers from the Near East. Journal of Anthropological Sciences. Vol. 86 (2008), pp. 143-163. He was buried with equipment of a hunter-gatherer including a fire stone knife, a fire stone core, another stone as hammer, a blade of fire stone, a bone tip, a pellet of ochre and Propolis (a resinous matter, produced by bees). Limestone platelets decorated with ochre drawings had been placed on top of the tomb. Villabruna is significant in terms of the history of population genetics: the remains were found to carry Y-DNA haplogroup R1b1a (R-L754). This is the oldest example documented of haplogroup R1b in Western Europe. Ripari Villabruna - Wikipedia.
R1b1 (R-L278*) (7640-7555 BP) The ‘Samara hunter-gatherer’ found is an adult male from grave 1 in a Neolithic-Eneolithic settlement producing artifacts from the Elshanka, Samara, and Repin cultures. The specific site is Lebyazhinka IV, on the Sok River, Samara oblast, Russia in the Volga region. Lebyazhinka IV and the neighboring Lebyazhinka V site were occupied seasonally by multiple cultures between 9000-5500 BP.
R1b (R-M269) a single male Bell Beaker R1b M269 from Quedlinburg, Germany dated to 6250 BP. An overview of sources from southern Germany concluded that Bell Beaker was a new and independent culture in that area.
R1b (R-M269) The remains of two males from a Bell Beaker German site at Kromsdorf dated to 6550 BP tested positive for R1b M269. It is known from other testing that R1b1a2 (R-M269) is the dominant branch of R1b in Western Europe.
R1b (R-M343) Lichtenstein Cave in Austria, near the border of Switzerland 1,000 BC - Out of the 19 males represented in the cave, 15 yielded the full 12 tested STR values, with 12 showing haplotypes related to I2b2 (at least four lineages), two to R1a (probably one lineage), and one to R1b predicted haplogroups. Mitochondrial haplogroups found included 17 from H, 5 from T2, 9 from U5b and 5 from J*.
R1b1a2 - King Tut (c.1341 BC - c.1323 BC) - A Swiss genealogy company named IGENEA issued a press release based on a blurry screen-grab from the Discovery documentary. It claimed that the colored peaks on the computer screen proved that Tutankhamun belonged to an ancestral line, or haplogroup called R1b1a2 [dated to 3340 BP], that is rare in modern Egypt but common in western Europeans. King Tut's DNA, By Analee Newitz.
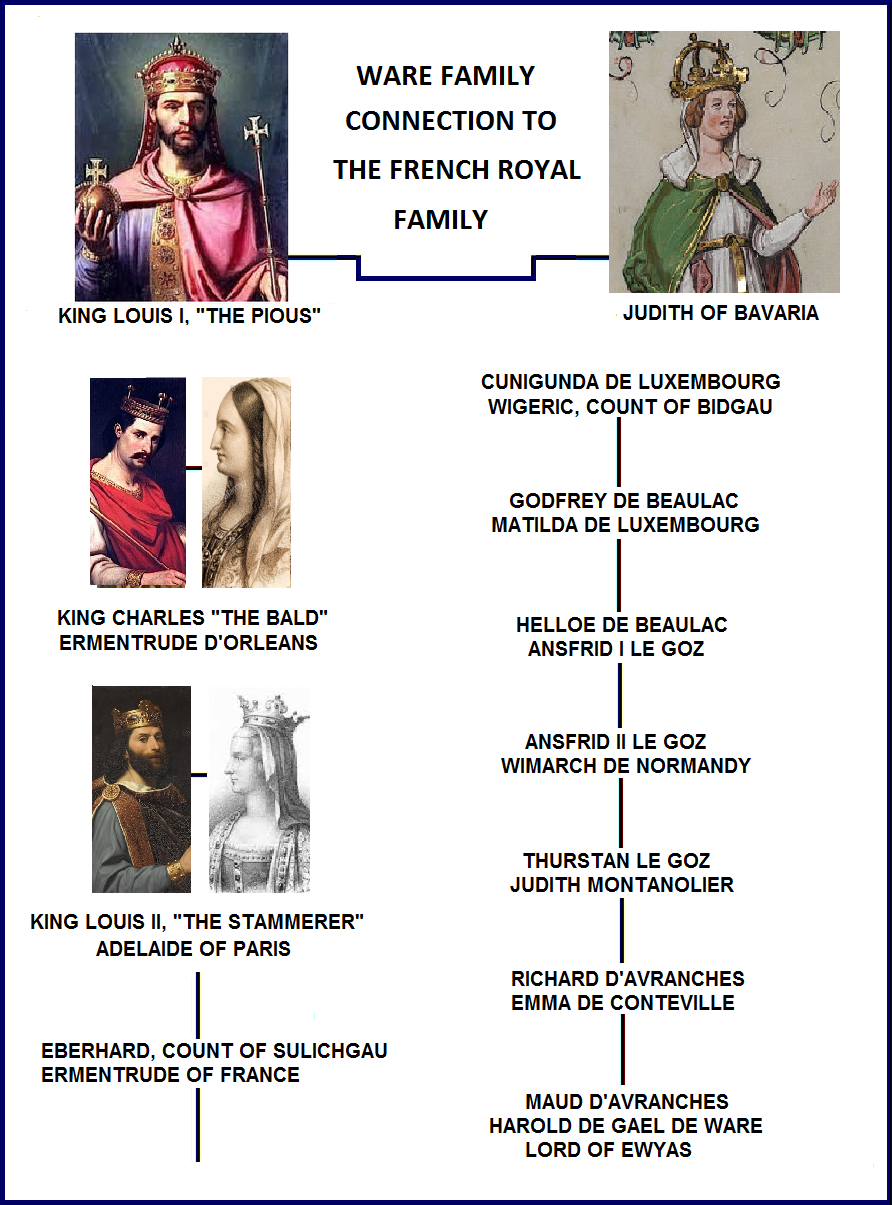
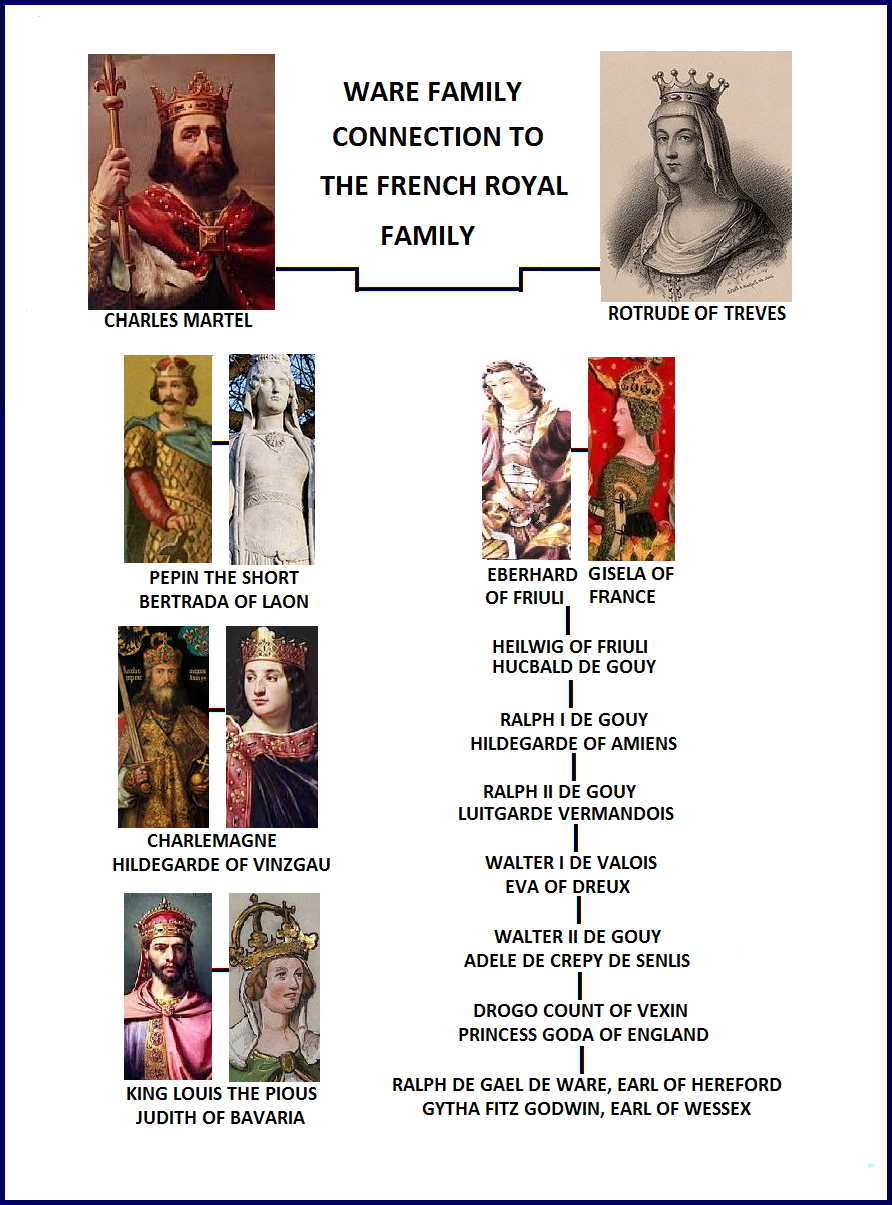
WARE LINEAGE TO THE ROYAL FAMILY